Legal Framework
Background on Electoral Legal Frameworks
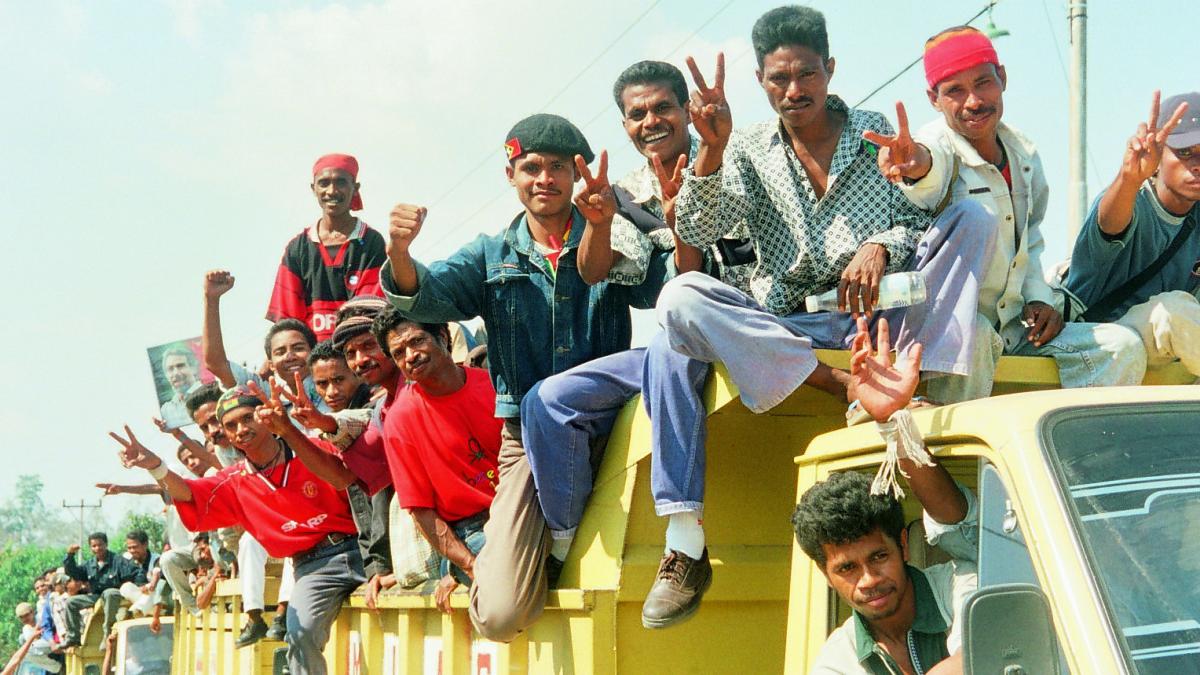

Electoral processes must be constituted in a legal framework. Electoral legal frameworks can be envisioned as a pyramidal hierarchy of constitutions, political/security agreements, legislation, regulations, and administrative procedures. The outcome of elections has a direct impact on who exercises authority in a given society. For this reason, it is necessary to establish a legal framework to ensure that authority will be transferred and to define, if any, changes to the scope of that authority.
Electoral operations are a highly technical exercise. Through the legal framework, detailed rules are needed to define the number of polling stations, procedures for voter registration, the distribution of electoral material, the scope of campaigns, ballot design or other procedures. An efficient functioning of rules will increase confidence in the electoral process. If this is not the case, some electoral stakeholders may perceive that the rules are biased against them and that the result is illegitimate.
The legal framework must also address potential security threats. These include criminal behavior (in general, any breaking of the electoral rules), which could hinder the conduct of elections through violence.
View the tabs under the Legal Framework section to find out details about the rules under which the East Timor referendum functioned and the circumstances that led to their development. For the Popular Consultation, the legal framework involves a series of political and security agreements and a set of administrative regulations developed and adopted by the U.N.